What is a Content Management System (CMS)?

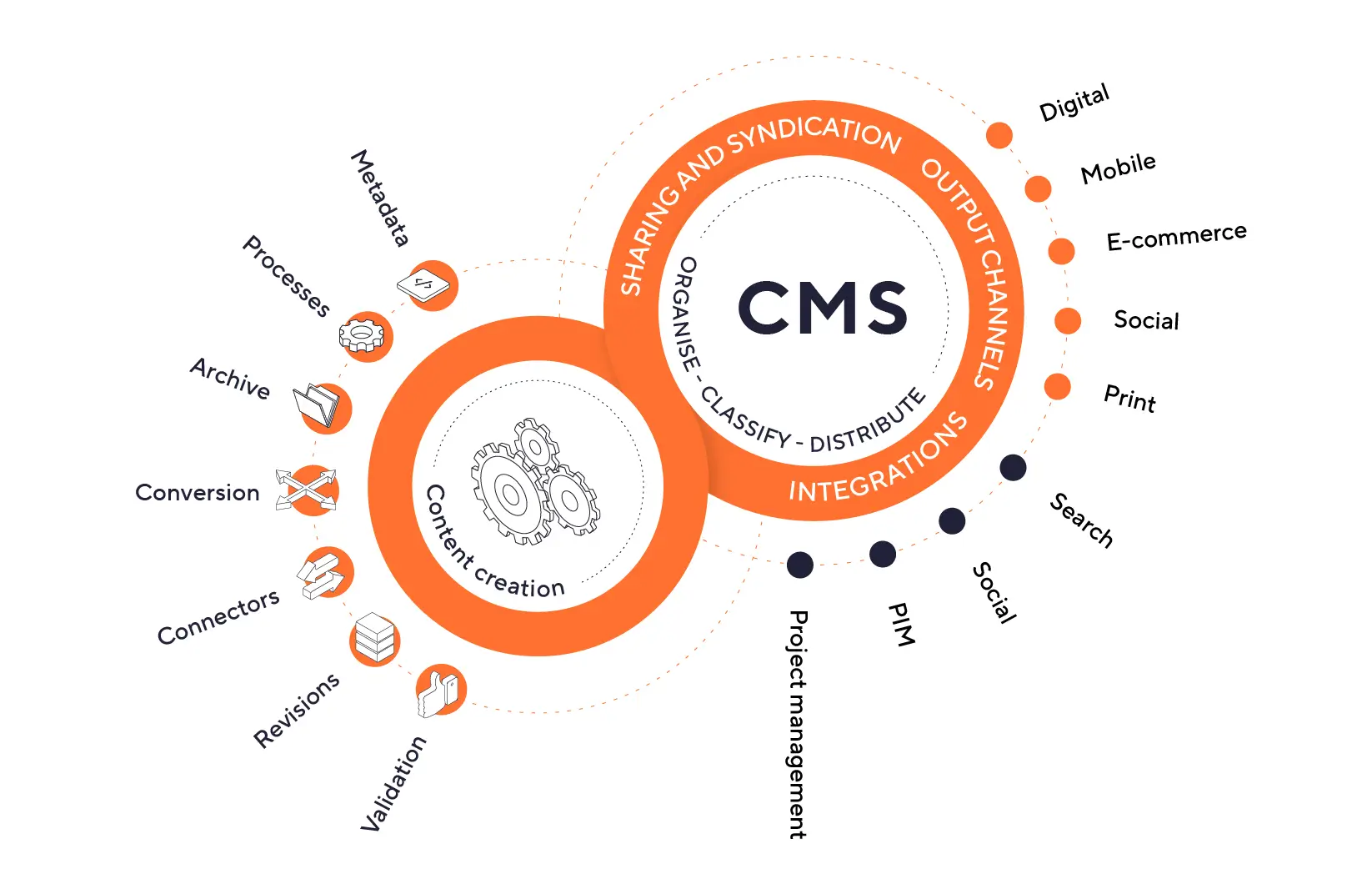
In the context of a master data management (MDM) solution, a content management system (CMS) allows companies to further enhance the variety of managed information (in addition to DAM assets and PIM product data) and extend the overall data management experience across the organization.
A CMS enables businesses to centralize all editorial content, product information, media files, mailings, newsletters, e-commerce sites, catalogs, brochures, and more on a single platform. The goal is to share resources across different departments and service providers seamlessly.
Definition of a Content Management System
Within the MDM ecosystem, the concept of a CMS goes beyond its traditional definition.
A CMS is commonly associated with WCM (web content management) tools, such as WordPress, Drupal, or Joomla. These tools are easy to install, cost-effective, and have become widely adopted enterprise solutions for managing corporate websites.
By definition, a content management system (CMS) is a software category that allows users to design, manage, and update websites or mobile applications dynamically. These systems are often referred to as dynamic content management systems (DCMS).
CMS platforms can be used by multiple users simultaneously, with roles and permissions assigned to manage content (e.g., administrator, contributor). They also help structure website content into categories, such as FAQs, blog articles, etc.
There are two main types of CMS:
- Open source CMS
- Proprietary CMS
Some of the most popular CMS platforms include:
- WordPress
- Drupal
- Contentful
- Strapi
- Storyblok
- Pimcore
Why use a CMS?
Because centralizing your data has never been easier. A CMS is the ideal tool for managing products, editorial content, websites (e-commerce or not), mailings, newsletters, and more — all with advanced features found in professional solutions.
This is where the DXP (digital experience platform) concept truly comes to life. A CMS allows businesses to manage, deliver, and optimize contextualized digital experiences, enriched by customer data management and analysis.
Thanks to its hyper-connectivity, a CMS can integrate seamlessly with third-party systems or applications, ensuring a consistent customer journey across all channels.
An enterprise CMS can manage multi-site setups, pre-production environments, and offer a wide range of features, such as editorial workflows or advanced business connectors (e.g., translation services, DAM-PIM connectors, etc.).
A CMS typically includes a page builder, enabling users to integrate content or digital assets directly from DAM or PIM systems.
As we’ve seen, website administrators often face content management challenges, making their tasks more complex. A content management system (CMS) provides a user-friendly interface that allows them to add, modify, and delete content directly within the platform.
In concrete terms, a CMS offers:
- Centralized administration
- Collaborative workflows
- Content timestamping
- Separation of content and design (templates)
- Access control
What are the benefits of a Content Management System (CMS)?
The benefits of a CMS are numerous. Here’s why you should consider using a CMS platform.
What is the added value of a Content Management System (CMS)?
As mentioned earlier, advanced programming knowledge is not necessary if your goal is simply to maintain an online presence. The true added value of a Content Management System (CMS) lies in its ease of use, allowing users to create their website and manage their content effortlessly.
A wide range of extensions (both free and paid) are available to enhance your website with new features. For instance, you can:
- Offer your content in multiple languages
- Include a contact form
- Share your articles on social media
- Add a chatbot
- Improve your SEO performance
Additionally, a CMS allows tech-savvy users to handle development functions for further customization, ensuring that the website reflects the brand’s identity.
What are the key challenges of a Content Management System (CMS)?
Within an MDM solution, one of the main challenges of a CMS is the ability to natively manage one or more websites, including those with different templates, in multiple languages. This is a major advantage for international companies.
When combined with various plugins (such as web-to-print tools, catalog automation, and print tools), the CMS becomes a comprehensive solution to manage all your content and data across your communication channels.
What is the role of a CMS within a company’s ecosystem?
When we look at the flow of information within the data lifecycle for marketing purposes, an effective strategy must be built around MDM (Master Data Management), incorporating the following concepts:
- DAM (Digital Asset Management) to organize and distribute media and documents
- PIM (Product Information Management) to qualify and aggregate product data
- CMS (Content Management System) as the brand portal
Within an MDM, product information is managed through the PIM, images and media are handled by the DAM, and content is managed via the CMS. All data is then centralized in one place, making it easier to access and distribute across various channels.
A CMS can retrieve data from the PIM or DAM to build web pages, ensuring consistent and enriched content for digital distribution channels.
Do you have a project?
Request your personalized audit today.
Need help with your CMS implementation?


